Industrial Endoscope: Utilizing Advanced Technology for Large Steam Turbines
Industrial Endoscope: Utilizing Advanced Technology for Large Steam Turbines
Introduction:
In the world of industrial machinery, the need for effective inspection and maintenance has always been crucial. This is particularly true for large steam turbines, which play a vital role in various industries such as power plants, refineries, and manufacturing facilities. To ensure the smooth operation and longevity of these turbines, regular inspections are essential. One invaluable tool that has revolutionized the inspection process is the industrial endoscope. In this article, we will delve into the applications and benefits of using industrial endoscopes for large steam turbines.
What is an Industrial Endoscope?
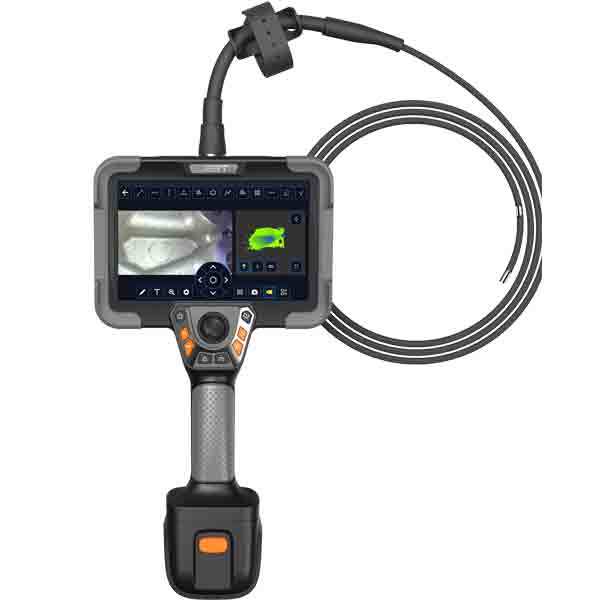
An industrial endoscope is an advanced inspection instrument consisting of a long, flexible tube with a high-resolution camera and light source. Its primary function is to provide visual access to hard-to-reach areas inside machinery and equipment. The endoscope allows inspectors to detect and assess any potential issues without the need for disassembling or shutting down the machinery.
Applications in Large Steam Turbines:
Large steam turbines are complex machines with numerous internal components. These turbines are subjected to extreme temperatures, rotational forces, and intense pressures, making regular inspections of critical components imperative. Industrial endoscopes are specifically designed to meet the demands of inspecting large steam turbines. Let's explore some of the key applications.
1. Blade Inspection:
The blades in a steam turbine are subjected to considerable stress due to high-speed rotation and exposure to steam. Industrial endoscopes enable inspectors to examine blades for any signs of damage, erosion, or cracks. By precisely maneuvering the endoscope, inspectors can capture high-definition images or videos of the blades' condition, helping identify potential faults and determine the need for maintenance or replacement.
2. Rotor Inspection:
The rotor is the central rotating component of a steam turbine, responsible for converting steam energy into mechanical power. Ensuring the integrity and efficiency of the rotor is vital for optimal turbine performance. Industrial endoscopes allow inspectors to visually examine the rotor's internal surfaces, looking for any signs of corrosion, pitting, or wear. Early detection of such issues enables proactive maintenance, minimizing downtime and extending the rotor's lifespan.
3. Casing and Sealing Inspection:
The casing and sealing systems of steam turbines prevent steam leakage and ensure efficient energy conversion. Industrial endoscopes can explore these critical areas to verify the integrity of seals, gaskets, and insulation. Inspectors can identify leaks, cracks, or foreign objects that may jeopardize the turbine's performance. By detecting and addressing these issues promptly, costly breakdowns or accidents can be avoided.
Benefits of Industrial Endoscope Usage:
The utilization of industrial endoscopes in large steam turbine inspections offers several noteworthy benefits.
1. Non-Destructive Inspection:
Traditional inspection methods often require dismantling machinery, which is time-consuming and costly. Industrial endoscopes provide a non-destructive inspection technique, reducing downtime and avoiding unnecessary disassembly.
2. Enhanced Visual Access:
The flexible nature of industrial endoscopes allows access to intricate and confined spaces within turbines. Inspectors can navigate through narrow passages and observe the condition of critical components with great precision.
3. Early Defect Detection:
By capturing real-time images or videos, industrial endoscopes facilitate early detection of defects or abnormalities. Timely maintenance interventions can be planned, preventing and minimizing the impact of potential failures.
Conclusion:
Industrial endoscopes have undoubtedly revolutionized the inspection process for large steam turbines. Their versatility, non-destructive capabilities, and ability to provide precise visual access contribute to improved maintenance practices. By utilizing these advanced technologies, industries can enhance the longevity and reliability of their steam turbines, ensuring sustained and efficient operations.