Videoscope for Turbine Inspection: Advancing Efficiency and Safety in Power Plants
The power generation industry plays a vital role in providing energy for various sectors, ensuring a steady supply for homes, businesses, and industries. Turbines are the driving force behind power plants, converting various forms of energy into mechanical power to generate electricity. As these complex machines operate continuously, regular inspections are essential to detect any potential issues and ensure their smooth functioning. Fortunately, with the advent of advanced technologies, videoscopes have become a valuable tool for turbine inspection, significantly improving efficiency and safety in power plants.
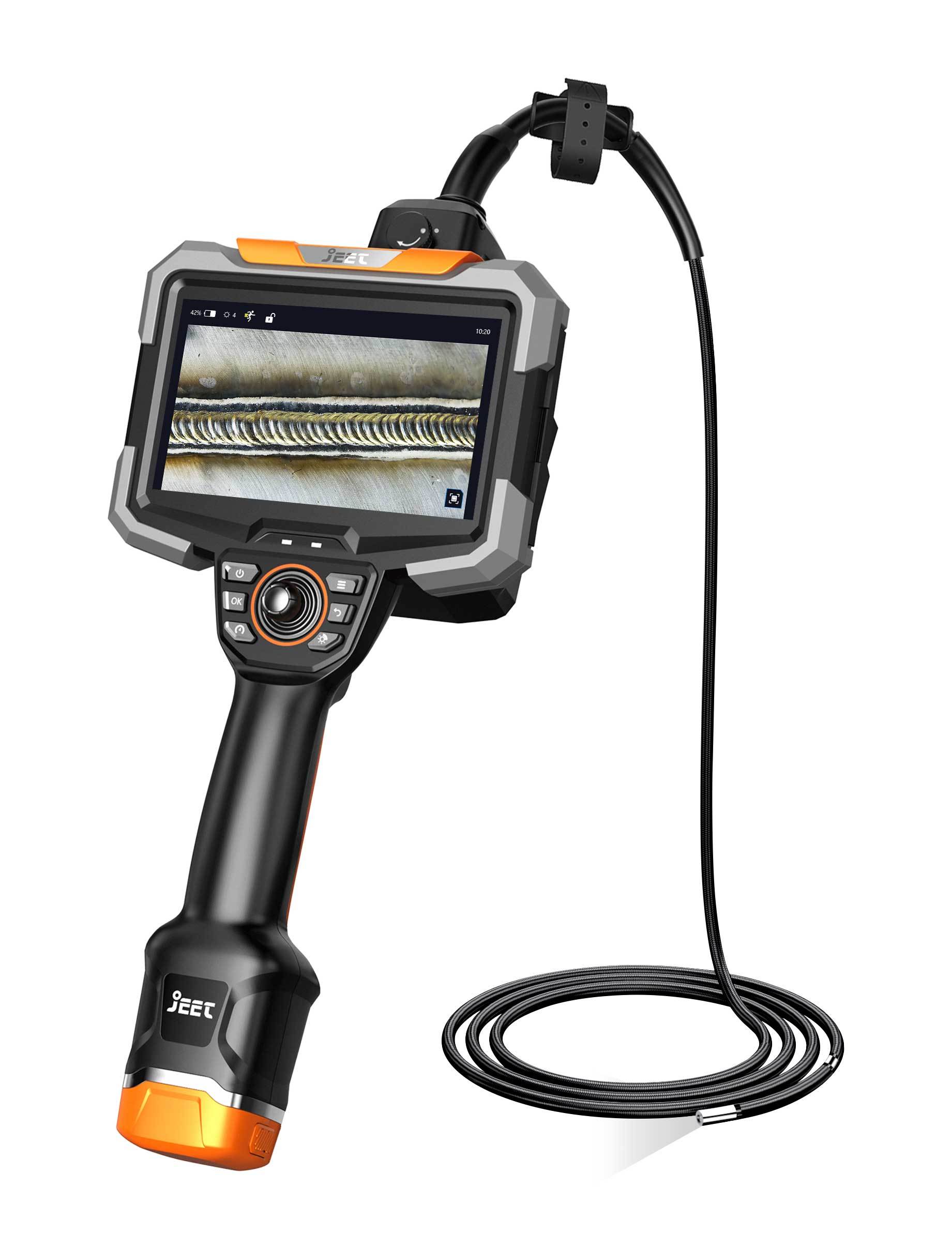
A videoscope is a cutting-edge inspection device that allows engineers and technicians to visually examine otherwise inaccessible areas within turbines. Equipped with a high-resolution camera mounted on a flexible insertion probe, videoscopes capture detailed real-time images and videos of the turbine's internal components such as blades, valves, combustion chambers, and casings. These images are relayed to a display unit, enabling the operator to assess the turbine's condition without the need for costly and time-consuming disassembly.
One of the key advantages of using videoscopes for turbine inspections is the ability to identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. As turbines operate under extreme conditions, they are susceptible to wear, corrosion, cracks, and foreign object damage. Videoscopes, with their high-definition imaging capabilities, can help detect these issues at an early stage, allowing for timely maintenance and repair, thereby preventing costly downtime and potential catastrophic failures.
The flexible insertion probes of videoscopes can be maneuvered through narrow passages and complex internal geometries within turbines, providing thorough visual inspection of all critical components. Engineers can easily navigate through bends, turns, and corners, capturing close-up views of areas that would otherwise be inaccessible. This comprehensive inspection ensures the detection of even the most minuscule defects, promoting overall turbine reliability and performance.
Additionally, videoscopes equipped with advanced features such as articulation and 360-degree rotational capabilities offer enhanced versatility and flexibility during inspections. The ability to manipulate the probe and adjust the camera angle aids in capturing detailed images from various perspectives, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of the turbine's condition.
When it comes to turbine inspections, safety is paramount. The traditional method of inspecting turbines involved physical entry into confined spaces, exposing technicians to potentially hazardous environments and risks. The utilization of videoscopes eliminates the need for personnel to enter these hazardous areas, significantly reducing the chance of accidents and injuries. Moreover, videoscopes are often equipped with integrated lighting systems, illuminating the inspection area and ensuring clear visibility in even the darkest corners of the turbine.
Videoscopes for turbine inspections also streamline the inspection process, reducing the overall time required for assessment. They eliminate the need for disassembling the turbine and erecting scaffolding structures, thereby minimizing downtime and increasing operational efficiency. Quick and accurate inspection results allow engineers to make informed decisions promptly, optimizing maintenance planning and resource allocation.
In conclusion, videoscopes have revolutionized the way turbine inspections are conducted in the power generation industry. Their ability to provide remote visual access to critical internal components, detect potential issues at an early stage, enhance safety, and streamline the inspection process has significantly advanced efficiency and safety in power plants. As technology continues to advance, videoscopes will undoubtedly play a crucial role in ensuring the uninterrupted generation of power and meeting the growing energy demands of our modern world.